Antiviral
Effective antiviral medications to help prevent and treat viral infections. Shop trusted brands for fast relief and better health support.
Antiviral medications play a crucial role in treating viral infections. These drugs help to reduce the severity and duration of illnesses caused by viruses. They do not cure viral infections but control symptoms and prevent complications.
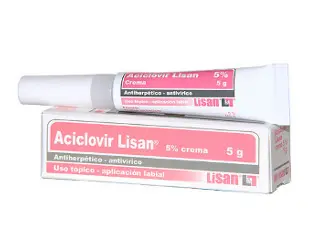
One of the most widely used antivirals is Aciclovir. It is effective against herpes viruses, including herpes simplex and varicella-zoster. Aciclovir is available in tablet form and as a topical cream, such as Acyclovir cream 5%. The cream is commonly used for cold sores and genital herpes. It helps in reducing pain and speeding up healing.
Famvir is another popular choice for herpes treatment. It contains famciclovir and is taken orally. Famvir works similarly to aciclovir but may have a longer half-life, allowing less frequent dosing. It treats shingles, genital herpes, and cold sores effectively.
Valtrex, or valacyclovir, is a prodrug that converts into aciclovir in the body. It is notable for its higher bioavailability. Valtrex is commonly prescribed for herpes simplex infections, shingles, and cold sores. It reduces viral shedding and accelerates recovery.
Zovirax is a brand name for aciclovir tablets and ointment. Zovirax ointment is widely used for cold sores. The tablet form treats herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster. Its long-standing use makes it a trusted option in antiviral therapy.
Copegus contains ribavirin and is used mainly for hepatitis C treatment alongside other drugs. It works by inhibiting viral replication. Due to its side effects, it requires close medical supervision during use.
Epivir and Epivir HBV contain lamivudine. These drugs treat hepatitis B and HIV infections. Epivir HBV is tailored specifically for hepatitis B, reducing viral load effectively and improving liver function.
Sustiva or efavirenz is an antiretroviral used in HIV treatment. It inhibits reverse transcriptase, an enzyme needed by HIV to replicate. Sustiva is part of combination therapies, improving patient outcomes significantly.
Rebetol is another antiviral used against hepatitis C virus. It is usually combined with interferon or other direct-acting antivirals. Rebetol helps by preventing the virus from multiplying, improving cure rates.
Plaquenil, also known as hydroxychloroquine, is used somewhat controversially for viral infections. It was explored for antiviral properties but is primarily an anti-inflammatory agent for autoimmune diseases. Its role in viral therapy is limited and should be guided by a doctor’s advice.
Symmetrel, or amantadine, is an antiviral effective against influenza A virus. It helps reduce post-infection fatigue and other symptoms. Due to resistance, its use has declined, but it still remains useful in some cases.
Molnunat is a less commonly known antiviral. It offers potential benefits in viral replication inhibition. The specifics of its use vary depending on viral strain and medical guidance.
Monoket is not typically classified as an antiviral. It acts as a vasodilator and is often used in cardiovascular diseases. Its inclusion in this category may be linked to adjunct treatment roles but not direct antiviral activity.
Aldara contains imiquimod. Although not a classic antiviral, it stimulates the immune system to fight viral infections and abnormal skin growths like warts caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). Aldara helps in clearing lesions without directly killing the virus.
When using antiviral drugs, adherence to prescribed dosages is crucial. These drugs can have side effects like nausea, headache, or fatigue. Doctors might adjust treatment depending on the patient's condition and virus type.
Antivirals vary in spectrum and mechanisms. Some block viral entry into cells. Others inhibit viral enzymes or replication processes. Choosing the right antiviral depends on the infection type, severity, and patient health.
Aciclovir, Famvir, and Valtrex are frontline drugs for herpes viruses due to their proven efficacy and well-known safety profiles. They help control outbreaks and reduce transmission risk.
Hepatitis C treatment relies on combination antivirals like Copegus and Rebetol. These improve clearance rates and reduce liver damage. Hepatitis B responds well to Epivir HBV by suppressing viral replication.
HIV management requires lifelong antiretrovirals such as Sustiva. These drugs reduce viral load to undetectable levels, improving quality of life and lowering transmission chances.
Influenza antivirals like Symmetrel act early in infection to reduce symptom duration and severity. Resistance concerns mean newer antivirals are often preferred now.
Topical antivirals or immune response modifiers like Acyclovir cream and Aldara serve localized infections or lesions. They provide targeted treatment with minimal systemic effects.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting antiviral medications. Diagnosis and virus identification are vital for effective treatment. Self-medication or incomplete treatment courses can lead to resistance or relapse.
In summary, antiviral medications are essential tools in managing viral infections. From herpes to hepatitis and HIV, these drugs improve outcomes and reduce complications. Understanding the specific uses, benefits, and risks of popular antivirals aids in better health decisions.